 Electus
ElectusUnderstanding electric car charging
Everything you need to know about charging an EV at home or at public stations.
Charging an electric car can be divided into three categories:
- Home charging
- Accelerated charging at public stations
- Fast charging at public stations
Home charging
Home charging is the most economical and practical solution for everyday use. Plug in your car in the evening and it will be ready the next morning. Depending on your daily mileage, different solutions are possible.
A domestic socket allows you to recover around 80 km of range (14.4 kWh) only during off-peak hours or 120 km overnight (19.8 kWh). This is the most economical solution and is more than enough for daily use.
A reinforced socket (e.g. Green’Up) is a stronger domestic socket allowing faster charging. This is the recommended solution for 90% of users. Its dedicated installation prevents overheating risks.
Using off-peak hours it allows you to recover 180 km of range (29.6 kWh) or 250 km (40.7 kWh) overnight.
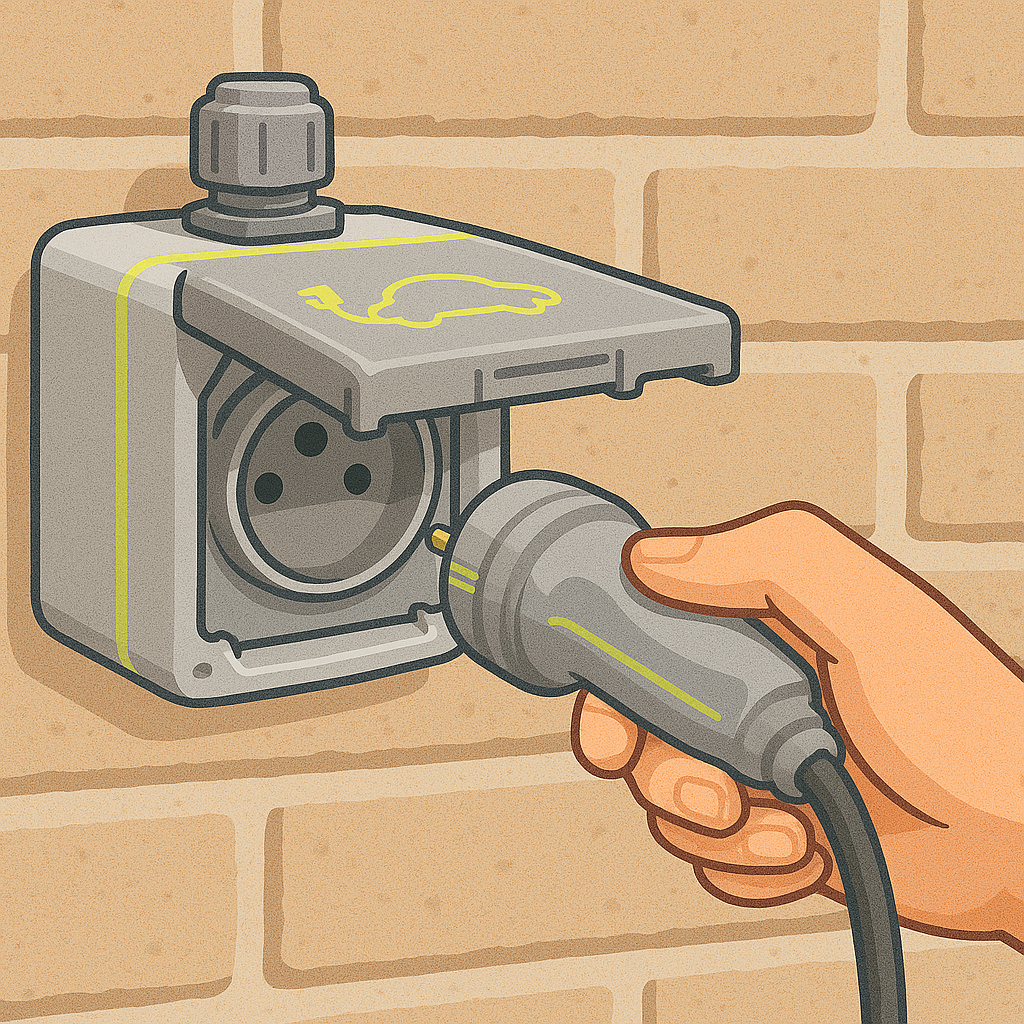
Your charging cable (with domestic plug) must support 16A to benefit from maximum power. This information is written on the back of the charger block.
To charge on a domestic or reinforced socket, you need to use the occasional charging cable (CRO) which may come with the car.

A 7 kW or 11 kW wallbox is the most practical but more expensive solution. It usually comes with a fixed cable, avoiding taking the cable out of the trunk each time.
With off-peak hours you can recover up to 350 km (7 kW, 56 kWh) or 550 km (11 kW, 88 kWh), and overnight up to 480 km (7 kW, 77 kWh) or 750 km (11 kW, 121 kWh).
A 7 kW charger is recommended for single-phase homes. For three-phase, prefer 11 kW. Before choosing, check our guide about home wallbox installation.
| Charging solution | Range gained (10pm-6am / 8pm-7am) | kWh gained (10pm-6am / 8pm-7am) |
|---|---|---|
| Domestic socket | 80 km / 120 km | 14.4 kWh / 19.8 kWh |
| Reinforced socket | 180 km / 250 km | 29.6 kWh / 40.7 kWh |
| Wallbox 7 kW | 350 km / 550 km | 56 kWh / 77 kWh |
| Wallbox 11 kW | 480 km / 750 km | 88 kWh / 121 kWh |
To find out the best option for your needs, use our simulator (coming soon).
Accelerated charging at public stations
Accelerated charging stations use alternating current (AC) and allow a full charge in 4 to 6 hours, depending on your car's onboard charger.
Example: a Tesla Model 3 has an 11 kW AC onboard charger. On a 22 kW station, the car will only accept 11 kW.
These chargers are often found in train station car parks, supermarkets or public car parks. They let you charge while you do other activities nearby.
You usually need to bring your own Type 2 to Type 2 cable (not to be confused with a domestic plug to Type 2 cable).

To start charging, take your Electus badge and swipe it at the reader.
Stations with several connectors may require you to select the connector before swiping.
Once identified, plug the cable into the station then into the car. If the station has a door, make sure to close it before starting.
When unlocking the car, charging may stop. It should resume automatically.
Once your session is finished, swipe your badge again. The station will stop charging and unlock your cable.
Unplug the connector from the station first then from the car. If the station has a door, make sure to close it.
Don’t forget to free up the spot once you’re done charging!
Fast charging at public stations
Need a quick top-up? Fast chargers let you charge from 10% to 80% in about 20-30 minutes.

These stations deliver direct current (DC). Maximum power depends on your car and the station. You don’t need to bring your own cable, it’s always attached.
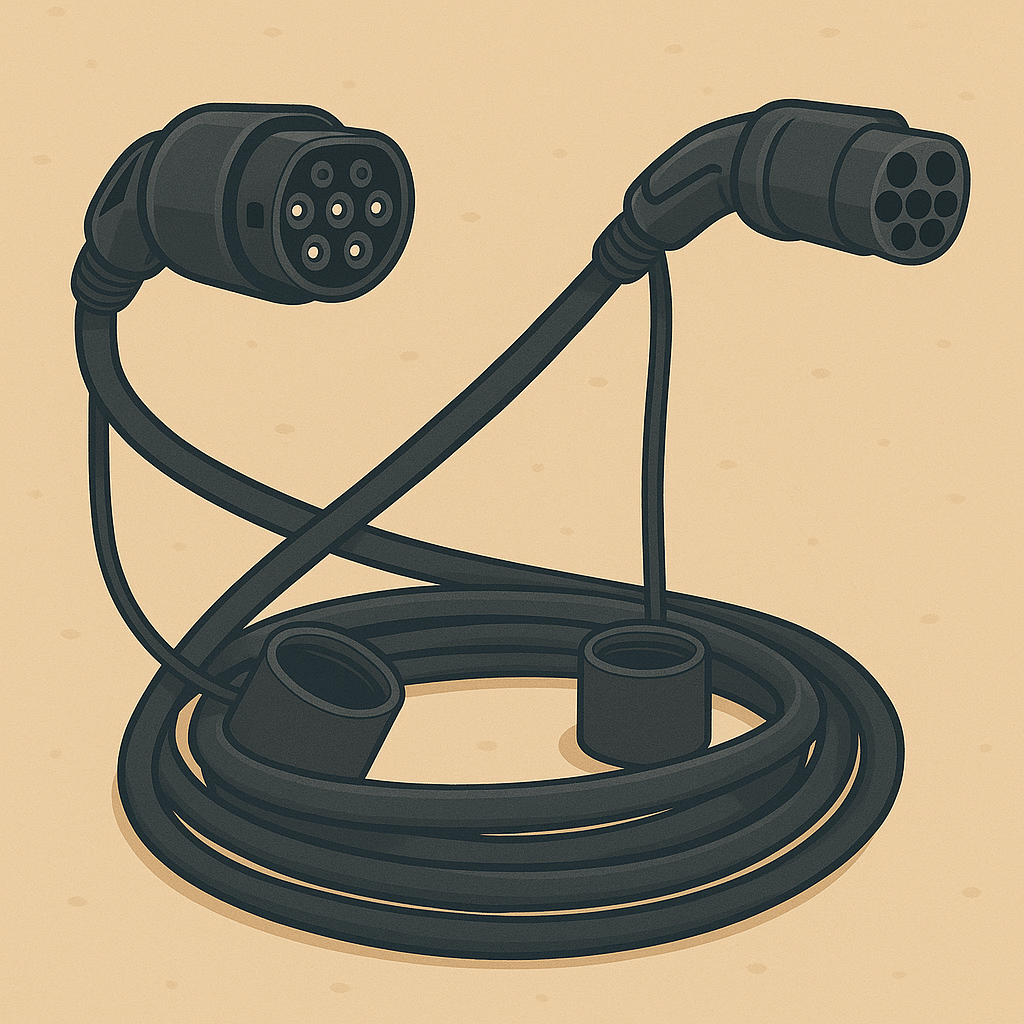
Some cars don’t support fast charging. To check, look at the charging port: it must have a CCS connector like in the illustration.
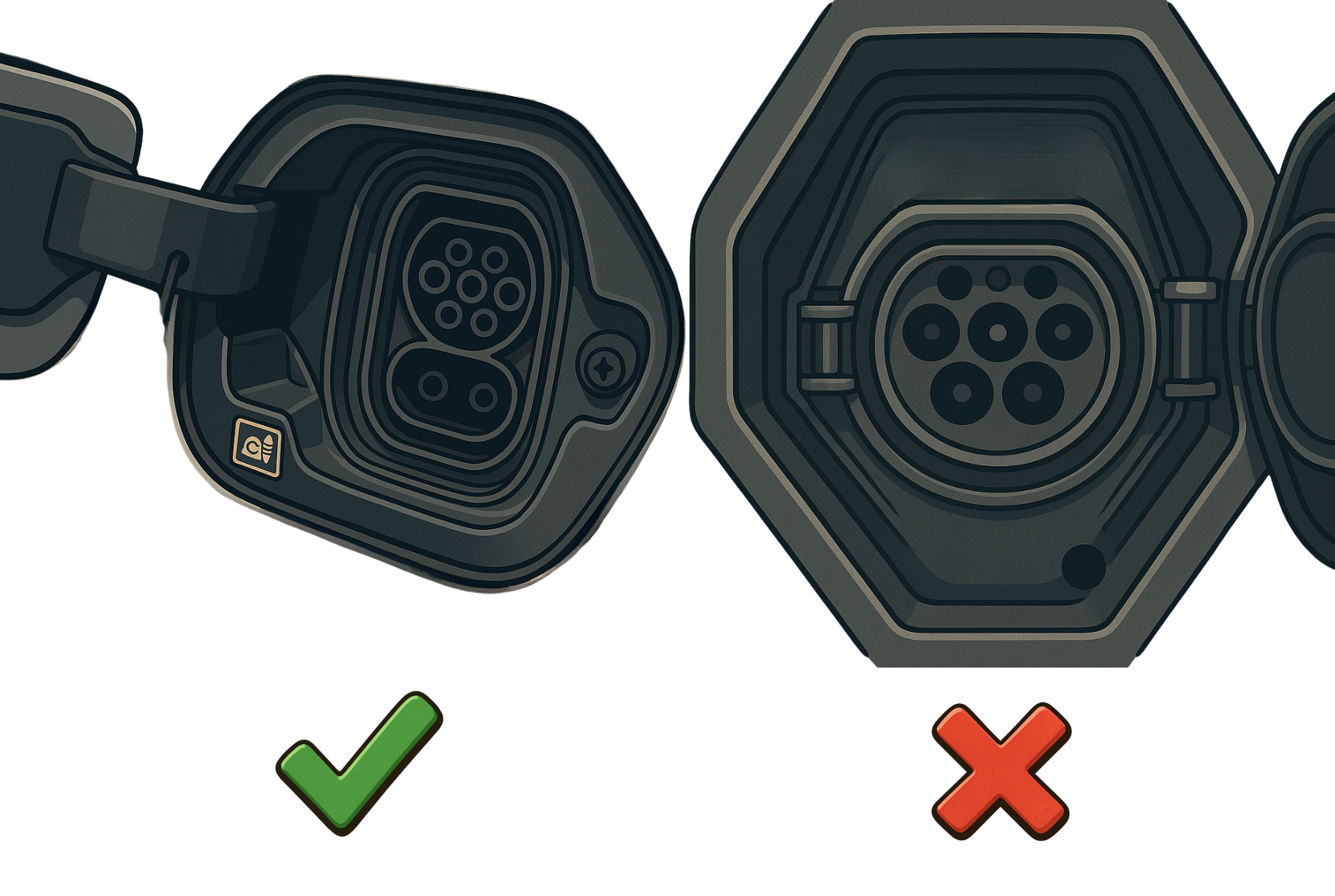

Unlike AC accelerated chargers, fast chargers provide DC power that goes straight to the battery without conversion.
Charging power depends on your car. To check your car’s max power, see our upcoming guide.
Example: a Tesla Model 3 supports 11 kW in AC and 170 kW in DC. On a 22 kW AC charger, it will accept 11 kW max (converted by the onboard charger).
On a 350 kW DC charger, it will take 170 kW max (directly to the battery).
During fast charging, power is highest when the battery is low. As it fills up, charging speed drops. Above 80%, speed falls sharply. On trips, unplug at 80% and keep going.
If the battery is cold, charging power may be limited. To avoid this, use battery preconditioning if your car supports it.
To start a fast charge, take your Electus badge (coming soon). Identify yourself at the station (select the connector first if required).
Plug the cable into your car.
The charge will start, wait a few seconds.
Some stations have several cables: use the CCS one (next illustration).

To stop charging, end the session and swipe your badge (some stations don’t require it). Put the connector back in place.
Don’t forget to free up the spot once you’re done charging!